Serverless¶
As mentioned in the introduction, if your requirements and use cases suit a serverless approach then this is also possible, further removing yourself from concepts like virtual machines and containers. An example architecture deployment is shown here.
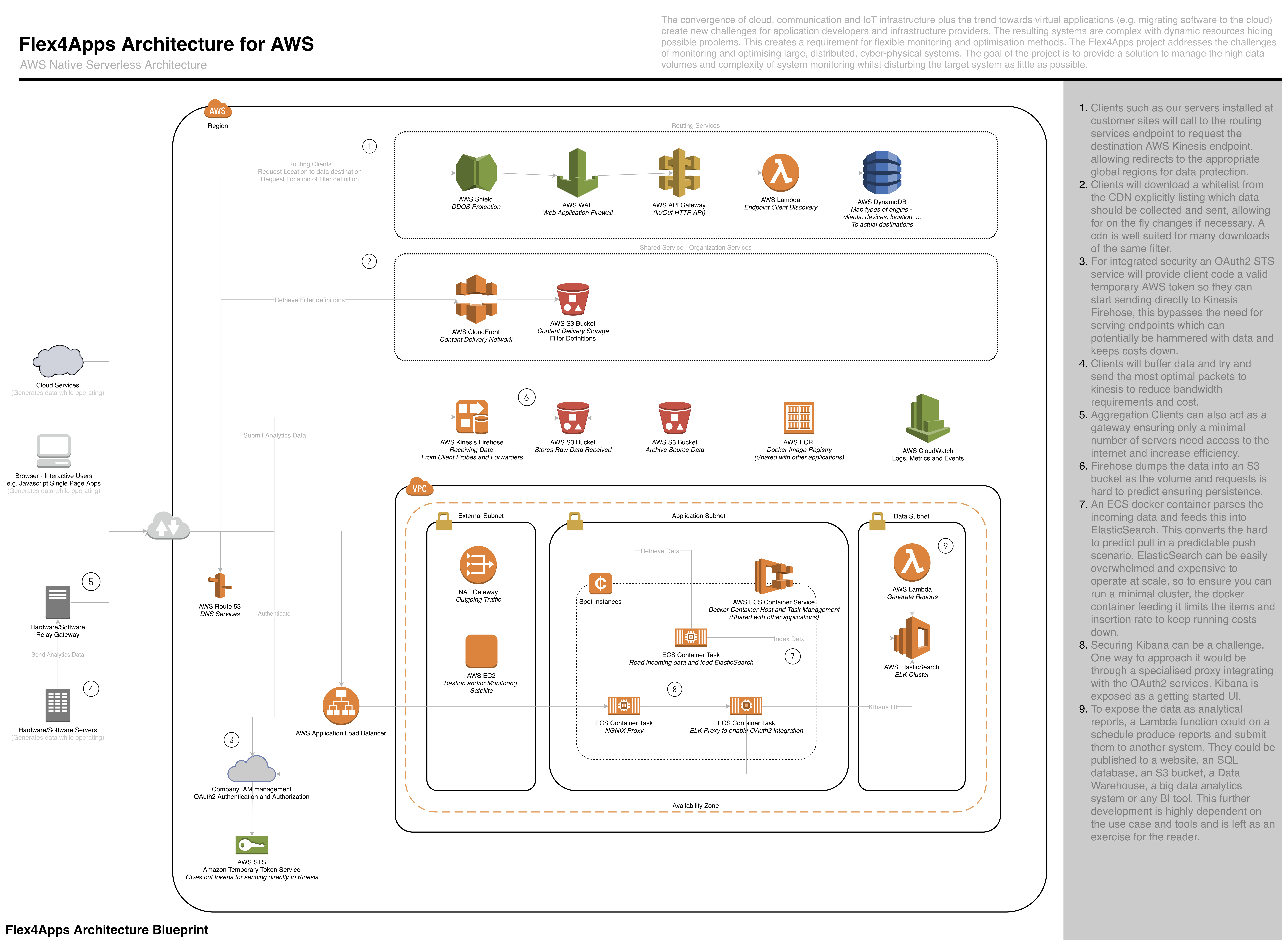
This example leverages a serverless setup by using the Amazon AWS cloud ecosystem, but similar approaches can also be implemented using Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud.
A pdf version of this image can be found in the source repository on github.
Example serverless analytics collection stack¶
Infrastructure Compnonents¶
Components:
- S3 backup bucket (analytics-[environment]-backup)
- Dynamodb user profile table (analytics-[environment]-user-profile)
- AWS Elasticsearch stack (analytics-[environment]-elasticsearch)
- Elasticsearch domain policy
- Cloudwatch log group: (firehose_logs)
- Cloudwatch log stream: (firehose_s3_log_stream, firehose_es_log_stream)
- Kinesis firehose delivery stream: (analytics-[environment]-firehose-delivery)
- Elasticsearch IAM Policy
- Elasticsearch IAM user and key
- Firehose IAM Policy and role
This entire stack is deployable through a single sls deploy command.
#to deploy
cd analytics-services
yarn deploy
Components:
- Lambda Functions
- DynamoDB Migrations
Project overview¶
This repo has the following main folders:
- analytics-services
- demo-app
analytics-services¶
This folder contains the setup of the entire analytics backend. This
- an api gateway that listens for a POST on /event, that accepts json data in the form of .. code-block:: json {user: “a userId”, event: “an event”, metaData: { json object containing meta data for the given event}}
- a lambda function that is triggered by the above incoming POST request and that updates the user profile and forwards the incoming record to a kinesis firehose.
- firehose stream that forwards incoming events to an elasticsearch cluster and S3 backup bucket
- the elasticsearch domain
- the S3 backup bucket for the raw data
- all the necessary iam policies
To deploy this backend, one needs to first install the serverless toolkit (https://serverless.com/). This framework is an easy tool that automates packaging and deploying lambda functions really easy. This toolkit is written in nodejs and requires a nodejs runtime to be installed. Note that the serverless toolkit does not require the lambda functions themselves to be written in nodejs.
Once nodejs is installed, install the serverless toolkit.
npm install -g serverless
Next, setup a AIM user on AWS that has enough rights to create and update the resources needed. Detailed documentation can be found at https://serverless.com/framework/docs/providers/aws/guide/credentials/.
Than, in the analytics-services folder, run
yarn install
to install project dependancies. Note that for the analytics services, this npm install will install both the dependancies required for the services itself, as well as some dependancies that are introduced in the serverless.yml project description file.
Next you can deploy the project using
yarn deploy
# or
yarn sls deploy -v
This last command will setup the entire infrastructure. Under the hood, serverless uses AWS Cloudformation, a dedicated service by AWS to describe and deploy entire “stacks” of resources. AWS Cloudformation is a free service, one only incures costs for the resources that are deployed within the stack. The lambda functions in this folder are developed in nodejs.
All resources that are deployed with the previous command are part of the mystage stage. One can deploy multiple environments using different stages (e.g. –stage prod for production).
yarn remove
will teardown the entire infrastructure.
One thing to note: Without special precaution, the API gateway end points that AWS Gateway returns are rather cryptic. (e.g. endpoints: https://hvd9fb2p5f.execute-api.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/devel/event). In order to have these endpoints in a more meaningful way (e.g. stats.mydomain.com), you will need to create an API Gateway domain. This can be done through serverless. (full documentation at https://serverless.com/blog/serverless-api-gateway-domain/)
This project includes the custom domain plugin that does this automatically. Since API Gateway only works with https, you’ll need to setup an ssl certificate. For that, you will need to use AWS Certificate Manager (https://aws.amazon.com/certificate-manager/). You can use your own certificates or have AWS handle that for you. AWS Certificate manager is a free service.
Setup your custom domain in AWS Certificate Manager, be sure to do that in the US-East-1 region (it will not work otherwise). Once that is done, you can setup your custom API Gateway domain through:
yarn sls create_domain --stage mystage
This can take up to 40 minutes.
If you use AWS Route 53 for your DNS, sls create_domain can update your DNS for you, you will need to edit the serverless.yml file for this. (For my demo, I’m not using Route 53)
Once your domain is up and running, simply redeploy using sls deploy --stage mystage
Deploy commands
cd analytics-services
yarn install
yarn sls deploy -v --stage mystage
To remove the stack: yarn sls remove -v --stage mystage
demo-app¶
This folder contains a small web application that can be used to send test events to the analytics stack. Be sure to edit app.js to post to the correct end point
Installation¶
- Serverless
npm install -g serverless
- Add credentials to the
.aws/credentialsfile - Do a
npm installin theanalytics-servicesfolder
Accessing kibana¶
When the analytics service is deployed, a IAM user is created with as only privilage that that user can access the elastic search cluster. An access key and secret are generated and published as output. In order to access kibana, the easiest solution is to run a local proxy server. Check https://github.com/abutaha/aws-es-proxy for details.
What I did:
wget https://github.com/abutaha/aws-es-proxy/releases/download/v0.4/aws-es-proxy-0.4-mac-amd64 -O aws-es-proxy
chmod +x aws-es-proxy
export AWS_PROFILE=esuser #be sure to add a esuser into your ~/.aws/credentials file, copy over access key and secret
./aws-es-proxy -endpoint https://<search-endpoint>.<region>.es.amazonaws.com
you can now go to http://127.0.0.1:9200/_plugin/kibana and access your kibana dashboards.
Note that you can also setup a proper login for Kibana, be sure to check: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/database/get-started-with-amazon-elasticsearch-service-use-amazon-cognito-for-kibana-access-control/
Unfortunately, at present it is not really possible to set this up in an automated fashion